Check valve in boiler: Structure, principle and application
Check valve is an important component in boiler systems, playing a role in controlling flow and preventing fluid backflow. It is an indispensable safety device, ensuring the efficiency and reliability of the system. This article will detail the structure, operating principle, classification, and installation of Check valves, along with their important functions in boiler systems and why check valves must be installed at the pump discharge.
Structure and Operating Principle of Check Valve
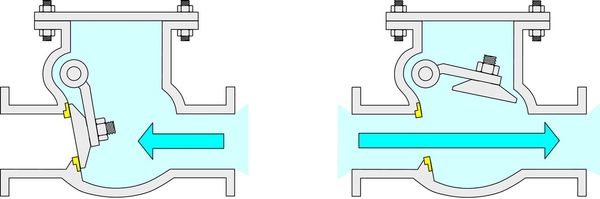
Operating principle of a swing check valve
A Check valve has a simple structure with three main parts: valve body, valve cover, and opening and closing mechanism. When fluid moves in the allowed direction, the valve opens to let the fluid pass through. When the pressure below is lower than or equal to the pressure above, the valve closes, preventing reverse flow.
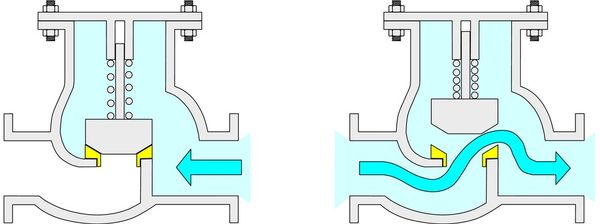
Operating principle of a disc check valve
Classification and Installation of Check Valves
Check valves are classified based on design, size, and material of construction. There are two common types of Check valves used in boilers: swing check valves and disc check valves. Each type has specific installation methods and applications, suitable for different types of systems and working environments.
To install a Check valve correctly, the first step is to inspect the valve and ensure its size fits the pipeline system. Check valves can be installed vertically or horizontally, depending on the system design and requirements.
Most Check valves have an arrow on the casing indicating the direction of water or fluid flow. During installation, attention should be paid to the flow direction because the valve only allows fluid to pass in one direction and prevents reverse flow. This helps protect the system from pressure reversal accidents and ensures stable operation.
- Before installation, clean the valve and pipelines to remove any debris that may cause obstruction.
- Then proceed to install the valve in the designated position, using appropriate tools such as wrenches and thread seal tape to ensure secure connections.
- Finally, check the entire system to ensure the valve operates correctly and there are no leaks.
These are the basic steps for installing a Check valve, but attention should also be paid to other factors such as flange face standards and threaded joint if the valve is connected in this way.
- For threaded valves, ensure that the valve threads and pipe threads match.
- For flanged valves, check the quantity and size of bolts as well as flange face standards to ensure safe and effective connections.
Improperly installed valves can lead to serious consequences such as equipment failure, reduced system efficiency, or even safety incidents. Therefore, adhering to proper installation instructions and conducting thorough checks after installation is crucial.
Functions of Check Valves in Boiler Systems
In boilers, Check valves play a crucial role in maintaining stable and safe operation. They prevent water and steam from the boiler from returning to the water supply pipes, thereby avoiding damage due to sudden changes in pressure and temperature. Additionally, Check valves help control flow in the system, ensuring that steam is evenly distributed to usage points.

Disc check valve installed on boiler feedwater line
Preventing Backflow: During steam production, Check valves are used to prevent the return of water or steam that has been separated from steam water. This helps maintain separation between liquids and gases, preventing contamination and ensuring the quality of steam produced.
Equipment Protection: Check valves play a crucial role in protecting equipment such as pumps, valves, and pipes in boiler systems. They prevent the backflow of steam or water, avoiding blockages and equipment damage.
Flow Control: By controlling the opening and closing operation of Check valves, operators can control the flow of steam or water in boiler systems most efficiently, enhancing performance and energy savings.
Avoiding Water Hammer: Another important advantage of Check valves is their ability to avoid water hammer. Water hammer occurs when the flow of liquid is suddenly stopped, causing high pressure that can damage the system. Check valves absorb and reduce this sudden pressure, protecting the system from damage.
Why Check Valves Must Be Installed at Pump Discharge

Check valve installed on water pump discharge
Installing check valves at the pump discharge helps protect the pump and boiler system from losses due to sudden pressure changes. When boiler pressure exceeds pump pressure, these valves prevent reverse flow from the boiler to the pump. They protect the pump from thermal effects from the boiler.
Furthermore, they also prevent reverse flow when the pump is not operating. Reverse flow is the motion where water, under the influence of gravity, flows back or through pipes opposite to its initial direction. To ensure there is always water in the pump for safe startup, check valves are always placed at the inlet and outlet of the pump.
Conclusion on the Benefits of Check Valves in Boilers
Check valves bring many benefits to boiler systems, from enhancing work efficiency to extending equipment lifespan. Investing in high-quality check valves is a smart decision, ensuring safety and efficiency for boiler systems.
Check valves are not only a part of boiler systems but also a symbol of safety and reliability in the industry. That's why understanding the structure, operating principles, and installation methods of Check valves is essential for any engineer working in this field.

